Table of Contents
MRI, which stands for magnetic resonance imaging, is a technique used to visualise tissues and organs under the skin. The MRI device is widely used to diagnose or to observe how well it responds to the treatment applied. Unlike computed tomography, this method does not make use of the harmful ionising rays of X-rays and is considered a more reliable imaging technique. MRI, which is mainly used to look at the soft tissue and nervous system, is a method used in the diagnosis of many diseases. It is essential in diagnosing cancer, infectious conditions, neurological diseases and damage assessment.
What is MRI (Magnetic Resonance)?
Magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging technology different from invasive methods in obtaining detailed 3D anatomical images. The device used for disease detection, diagnosis or treatment follow-up has advanced technology. MRI technology provides detailed imaging of organs and tissues by detecting the change in the direction of the axis of rotation of the protons in the atoms in the water structure that make up living tissues.
MRI Scanners are mainly used for imaging the body’s boneless parts and soft tissues. This method, which does not use the harmful ionising radiation of X-rays, differs from computed tomography and provides more explicit images. It can be used for detailed examinations of the brain, muscles, heart and blood vessels.
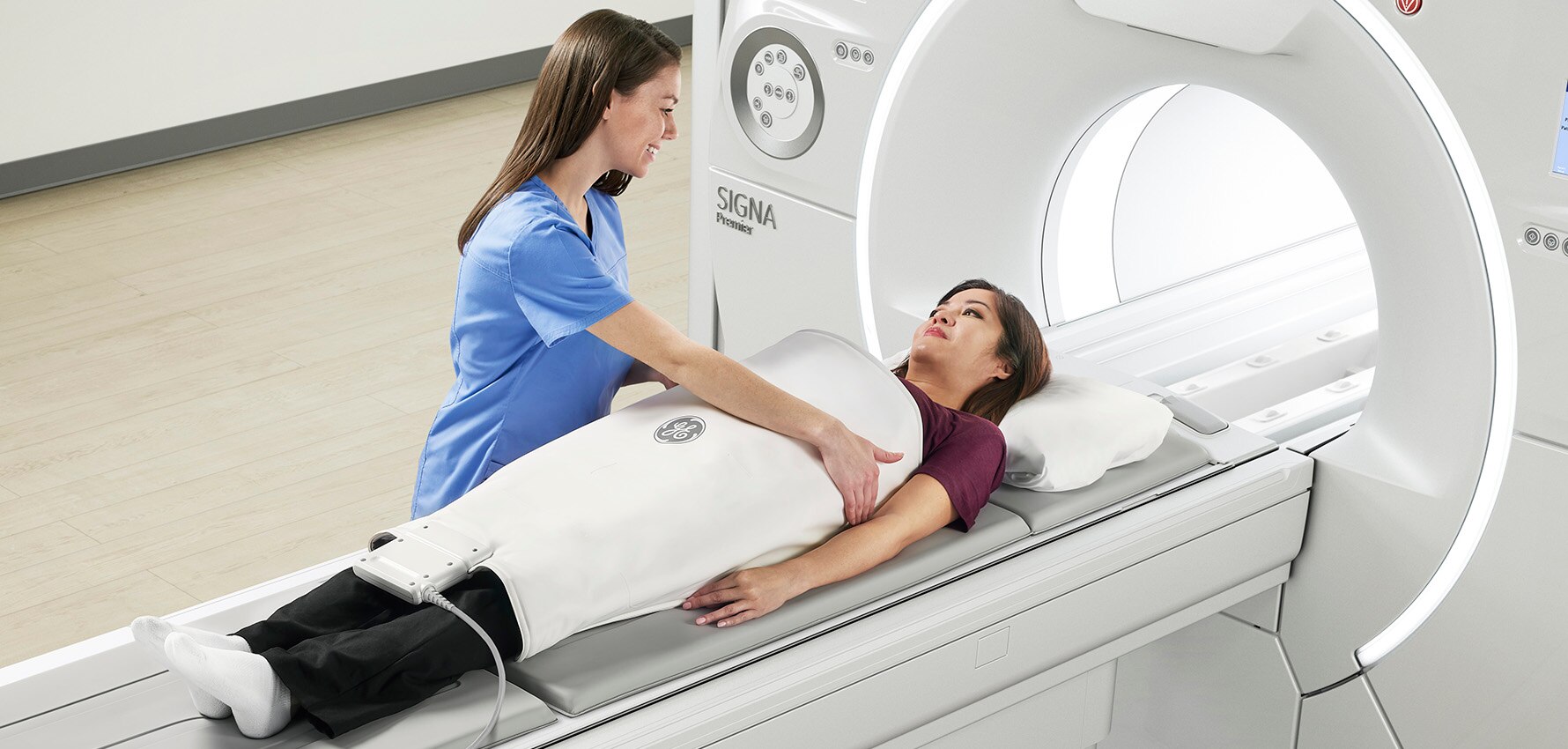
To take an MRI image, the patient can be thought of as being placed inside a giant magnet. For the images obtained to be clear, the patient must remain motionless during the shooting period. The patient is immobilised with tapes or special apparatus. In a device that uses the speed of the protons to align with the magnetic field, contrast agents can improve image quality or perform a faster process. The faster the protons are realigned, the higher the image quality and the more detailed the examination.
Compared to X-rays and computed tomography, MRI does not emit ionising radiation but uses a strong magnetic field. Therefore, the patient’s health status must be accurately assessed before the scan. People with implants such as pacemakers, vagus nerve simulators, insulin pumps, deep brain simulators or endoscopy capsules are unsuitable for MRI. Women with suspected pregnancy or who are pregnant are not recommended to undergo magnetic resonance imaging for the first 3 months. Therefore, if the physician requests Magnetic Resonance Imaging, the patient should share all information about their current health status with their physician.
Diffusion MRI
Diffusion MRI, a unique magnetic resonance scanning method, is used to examine water molecules in the body. This technique, which allows the random movement of water molecules in the tissue to be measured, is applied to detect changes or pathologies at the cellular level. Diffusion magnetic resonance is becoming increasingly crucial in stroke detection, tumour evaluation, diagnosis of infections, brain injury evaluation and investigation of neurological diseases.
Contrast-enhanced MRI
It is a magnetic resonance scan using contrast material or contrast agent. The contrast agent can be used to detect differences between tissues more clearly. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance can also be used to visualise specific structures better. It can be used for tumour detection and characterisation, examination of the structure of blood vessels, detection of infections, monitoring of inflammatory conditions and examination of the central nervous system. In contrast-enhanced MRI scans, a substance is injected intravenously. After the substance enters the bloodstream, it passes between the vessels and tissues, and the fluid accumulates more in the abnormal areas. Thus, these regions become more prominent and can be evaluated more efficiently.
Brain MRI
Brain Magnetic resonance examines brain tissue, lesions, brain tumours or other pathologies. Magnetic resonance of the brain can be performed with or without contrast. If it is performed with contrast, more detailed information about the brain can be obtained. In some cases, the doctor may request both images to be performed. In such cases, the non-contrast scan is performed first. After the scan, contrast dye is administered intravenously to the patient, and a contrast-enhanced scan is performed.
Spine MRI
A spinal MRI evaluates the spinal cord, discs, vertebrae, and other structures. It is used to diagnose back pain, spinal cord injuries, and spinal tumours. In some cases, a neck MRI may also be included.
Joint MRI
This type of magnetic resonance examines joints, joint ligaments, muscles, and surrounding tissues. It is a method generally used to diagnose and treat sports injuries. Based on the findings, whether the patient needs surgical intervention can also be diagnosed.
Abdominal MRI
Abdominal magnetic resonance is a filming method used to examine organs in the abdominal region, such as the liver, kidneys, pancreas, and intestines. Tumours, cysts, infectious conditions, and intra-abdominal problems can be detected during abdominal magnetic resonance.
Pelvic MRI
Pelvic MRI scans are performed to examine the lower abdominal organs such as the uterus, ovaries, prostate and bladder. It is an imaging method that can be used in the diagnosis of reproductive organ diseases, pelvic pain and cancer.
Breast MRI
It can be applied to examine breast tissue in detail and diagnose breast cancer. A firm diagnosis can be obtained in combination with the results obtained with breast mammography and ultrasound.
Cardiac MRI
It examines the heart and blood vessels. Cardiac MRI investigates the function of the heart muscle, visualises the structure of the heart valves and vessels, and assesses blood flow.
Vascular MRI
It is used to examine blood vessels. It is an imaging technique used to evaluate the presence of atherosclerosis, dilated blood vessels (aneurysms) and other vascular problems.
Spectroscopy MRI
MRI techniques can also be used to analyse chemical components in the body. This evaluation may be necessary, especially for examining brain tumours and metabolic disorders. At this point, the required analyses can be performed with spectroscopy MRI.
Functional MRI
Functional MRI examines brain activity. It is essential in investigating cognitive functions by showing the activation of specific brain regions. Different types of MRI can be used for other parts of the body. The doctor decides which MRI scan to use depending on the patient’s health condition. The findings can be used to diagnose the disease or determine how the current treatment works.
Situations where MRI is used
An MRI helps doctors diagnose a disease or injury and allows them to monitor how well the treatment is progressing. MRI machines can be used for different parts of the body. The diseases that can be diagnosed vary according to the area to be filmed. The regions examined and the diseases screened can be listed as follows. MRI of the brain and spinal cord can detect the presence of the following diseases
- Aneurysm
- Brain damage
- Cancer
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Spinal cord injuries
- Paralysis
- Inner ear problems
- Eye problems
When the structure of the heart and blood vessels is analysed, the following diseases or health conditions are assessed.
- Blocked blood vessels
- Damage caused by a heart attack
- Heart diseases
- Pericarditis (inflammation of the tissue surrounding the heart)
- Problems with the aorta, the main artery of the body
- Problems with the structure of the heart
MRI is also used to examine bones and joints. The presence of the following diseases can be questioned with the shots to be taken:
- Arthritis
- Bone infections
- Bone cancer
- Joint damage
- Disc problems in the spine
- Nerve problems that can cause neck or back pain
MRI scans can also be used to check the health of organs and for general health screening. The breast, liver, kidneys, pancreas, ovaries, and prostate can be scanned by MRI, and their current health status can be evaluated.
How is MRI (magnetic resonance ) taken?
A classic MRI machine is shaped like a giant tube with holes at both ends. A magnet surrounds this tubular tube. Patients lie on the bed placed in the middle of the tube, and the location of the person is fixed so that the relevant area to be shot is inside the device. Only the scanned part of the body is inside the machine, while the other part is outside the machine. After ensuring the necessary position, the shooting is started. In the case of contrast MRI, contrast dye is injected into the patient through a vein in the arm or hand. Thanks to this dye, the structures in the body can be seen more clearly. The principle of MRI is based on creating a strong magnetic field. A computer connected to the device receives the signals from the MRI and uses them to create a series of images. Each of the resulting photos shows a thin slice of the body. Having an MRI can be stressful for some people because of the noises it produces and the confined space inside the device. In such cases, some patients may be sedated. Thus, the scan can be performed under easier conditions. During the test, a loud banging or tapping sound is heard. This sound produced by the device is considered normal, and there is no reason for patients to panic. The sound is caused by the device generating energy for taking photographs. In some cases, earplugs or earphones can be used to muffle the sound. The duration of the scan to be performed varies depending on the application area or whether there is a contrast scan.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Minutes Does MRI Take?
The duration of the MRI scan varies depending on the area to be scanned and whether the scan is contrasted or not. The shooting time can last from 20 minutes to 90 minutes.
When is the MRI Result?
When the magnetic resonance imaging scan results are available, they may vary according to some factors. The type of MRI performed, the number of regions scanned or the interpretation of the results may affect the time it takes for the test results to be available. The workload of the radiologists at the health institution where the procedure is performed may also increase the waiting time. While the observations during the shooting constitute the first step of the results, complete interpretation and reporting is usually between 1 and 3 days.
What is done after an MRI?
After the MRI scan, some steps are followed to evaluate the procedure results and determine the necessary treatment or follow-up steps. The radiologist serving within the MRI imaging centre of the relevant health institution examines and reports the findings obtained. The doctor evaluates the report prepared by the radiologist and provides the necessary information to the patient. If any health problem is diagnosed, treatment planning is made for the patient and the treatment process is started.
Can Pregnant Women Use MRI?
MRI is an imaging method without side effects. This feature is a method that can be used safely for diagnostic purposes, even in tiny babies and pregnant women. Nevertheless, care should be taken not to use it in the first 3 months of pregnancy unless necessary. Scientific studies show that MRI is one of the safest imaging methods during pregnancy. However, in some MRI scans, a contrast agent called Gadolinium is used intravenously. MRI imaging using contrast material is not recommended during pregnancy.
Does MRI Contain Radiation?
During MRI scans, ionising radiation rays that harm health are not used. MRI scanning uses magnetic fields and radio waves. With these waves, it can create detailed images inside the body. MRI scanning is considered an essential diagnostic method for many diseases. The patient can be diagnosed correctly, and ideal treatment plans can be made thanks to detailed scans.