Table of Contents
Cancer Diagnostic Imaging
Various technologies are used to obtain internal body images, including those for cancer diagnosis. These images help doctors detect tumours, assess the extent of the disease, and plan treatment. The most commonly used methods are radiography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET).
Cancer diagnostic imaging is an essential tool for early cancer detection. Specialists can accurately determine the presence, location, and size of tumours using advanced imaging technologies. Early detection is crucial for achieving better patient outcomes and effective treatment.
Diagnostic Imaging
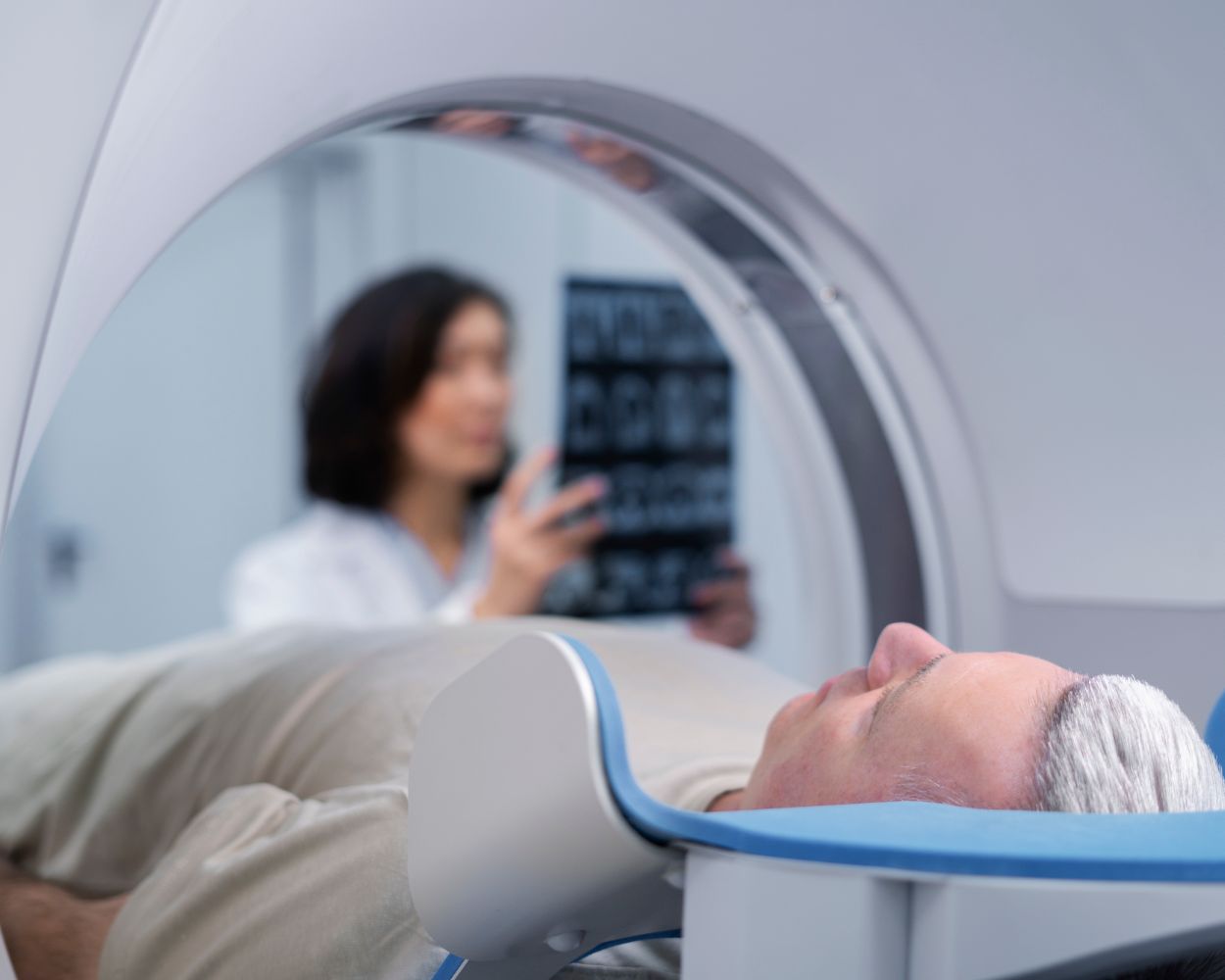
The most advanced technology is used in diagnostic imaging to generate internal body images. The most commonly used methods are ultrasound, X-rays, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These images help doctors diagnose various conditions related to organs and bone injuries, making imaging a vital part of healthcare. Unirad Lietuva provides affordable, fast, accurate, and reliable MRI services.
Each imaging method has its benefits and applications. For example, MRI provides better soft tissue images than radiography. Doctors often use ultrasound scans to assess the condition of organs and monitor pregnancy progress. These methods help accurately diagnose conditions and develop effective treatment plans.
To register for MRI services, contact us at (+370) 61-471-600 or visit the Baltic American Clinic at Nemenčinės pl. 54a, LT-10103 Vilnius.
Transmission Imaging
Transmission imaging is a technique where radiation passes through the body to create images. This method, usually performed using X-rays, allows doctors to visualize certain tissues and bones better. It is often used to check for infections, fractures, and other conditions.
During transmission imaging, the body absorbs varying amounts of radiation. Dense materials like bones absorb more radiation, appearing white in images, while softer tissues appear grey. This contrast allows for the accurate diagnosis of medical conditions.
Radiography
X-rays, a form of radiation, are often used to capture internal body images, most commonly to assess injuries like fractures. Additionally, X-rays help identify diseases and infections.
Computed Tomography (CT)
CT scans, also known as tomographic examinations, use X-rays and advanced computer technology to create images of body structures. This imaging method provides detailed images of bones, organs, and soft tissues, making it crucial for diagnosing cancer, fractures, and internal injuries.
Bone Scanning
Bone scanning is a medical imaging technique used to detect various bone conditions and diseases. A small amount of radioactive material is injected into the bloodstream, accumulating in the bones. Specialized cameras capture the radiation emitted by the bones, creating detailed images to detect cancer, infections, abnormal bone development, and fractures or arthritis.
Lymphangiography
Doctors also use a technique called lymphangiography to visualize the body’s lymphatic system. It involves injecting a contrast dye into vessels, typically in the hands or feet. X-ray images are then taken to track the dye’s movement through the vessels, identifying problems like lymphedema or blockages in the lymphatic system.
Mammography
Mammography is an X-ray of the breast used to detect breast cancer. It can identify tumours too small to be felt. Mammograms are most often prescribed for breast cancer screening or evaluating symptoms such as lumps or changes in breast tissue. Early detection through mammography can lead to better treatment outcomes and longer survival rates. Unirad Lietuva provides affordable, fast, accurate, and reliable mammography services. To register for mammography services, contact us at (+370) 61-471-600 or visit the Baltic American Clinic at Nemenčinės pl. 54a, LT-10103 Vilnius.
Reflective Imaging
Ultrasound imaging, also known as reflective imaging, uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of body structures. A transducer, a device that emits and receives sound waves, interacts with tissues and organs. These echoes are converted into data that healthcare professionals use to evaluate medical conditions without exposing patients to radiation. Reflective imaging is most commonly used to examine organs like the heart, liver, and uterus, as well as to monitor fetal development during pregnancy.
Due to its accessibility and safety, reflective imaging is widely used because it is non-invasive and painless. It allows medical professionals to observe movement in real-time, such as blood flow through vessels or the beating of the heart. Reflective imaging helps diagnose and monitor conditions such as gallstones, tumours, and abnormal fluid accumulation, providing detailed images in real-time. It is an essential tool in both diagnostic and therapeutic medical fields due to its adaptability and ability to capture dynamic processes.
Emission Imaging
Emission imaging is a technique used to capture signals emitted by the body after the introduction of a contrast substance. This method allows the observation of how organs function and moves in real time. PET imaging (positron emission tomography) is an emission imaging technique. During a PET scan, a small amount of tracer substance is injected into the bloodstream, accumulating in organs and tissues. The scanner detects the radiation emitted, creating images that show how organs and tissues function.
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) uses a gamma camera to monitor gamma rays emitted by a tracer substance introduced into the body. This method creates visual images showing the tracer’s movement in the body, aiding specialists in diagnosis.